Q.6 Describe the physical and aesthetic features of Sanchi Stupa-I.
Ans. The Sanchi Stupa-I, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is an iconic Buddhist monument known for its architectural brilliance and intricate artistry. It reflects the rich cultural and religious heritage of ancient India.
Physical and Aesthetic Features:
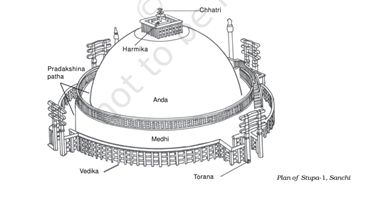
- Mahastupa (Great Stupa): Hemispherical dome (Anda) housing Buddha’s relics.
- Stone Covering: Originally brick-built, later covered with stone slabs.
- Toranas (Gateways): Four intricately carved gateways inspired by bamboo crafts.
- Carvings: Depict shalabhanjika, Jataka tales, and symbolic motifs.
- Pradakshina Patha: Unique upper and lower circumambulatory pathways.
- Ashokan Pillar: Features inscriptions and the Lion Capital.
- Harmika and Chhatra: Square railing and umbrella atop the dome.
- Expansion: Enlarged during the Shunga period with stone slabs.
- Southern Entrance: First gateway completed, adorned with statues.
- Schism Edict: Sandstone pillar with Ashoka’s inscriptions.
| Source: Fine Arts 11th Class: Chapter 4 : page Number : 29 |
| Keywords : Mahastupa, Stone Covering, Toranas, Carvings, Pradakshina Patha, Ashokan Pillar , Harmika and Chhatra |
| Extra Info: Mughal Architecture: Synthesis of Styles:Blend of Persian and Indian elements.Reached zenith during Mughal era. Key Features:Use of red stone and marble.Decorative inlay work (pietra dura).Arches, minarets, domes, and gardens.Sculptures of living beings (elephants, lions, birds). Major Structures:Humayun’s Tomb: Precursor to Taj Mahal, red stone, garden setting.Akbar’s Era: Agra Fort, Fatehpur Sikri (Buland Darwaza, Salim Chishti’s Tomb, Jodha Bai’s Palace).Jahangir’s Era: Itimad-ud-Daula’s Tomb (marble), Akbar’s Mausoleum.Shah Jahan’s Era: Taj Mahal, Red Fort, Jama Masjid.Gardens:Shalimar Gardens (Kashmir and Lahore).Gardens around tombs and buildings.Legacy:Profound influence on later Indian architecture.Integration of courtyards, pillars, and intricate designs. |
